Ukraine News: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine presents a multifaceted crisis, impacting not only the nation itself but also global politics, economics, and humanitarian efforts. This report delves into the key aspects of the situation, from the evolving military dynamics and the devastating humanitarian consequences to the international response and the far-reaching economic repercussions. We will explore the complexities of information warfare, the scale of the refugee crisis, and the long-term challenges of reconstruction and accountability.
The situation remains fluid, with daily developments significantly shaping the narrative. Understanding the interplay of military actions, humanitarian needs, international diplomacy, and economic consequences is crucial to grasping the full scope of this complex crisis. This report aims to provide a clear and concise analysis of these interwoven elements, offering insights into the present and potential future trajectories of the conflict.
The Current Military Situation
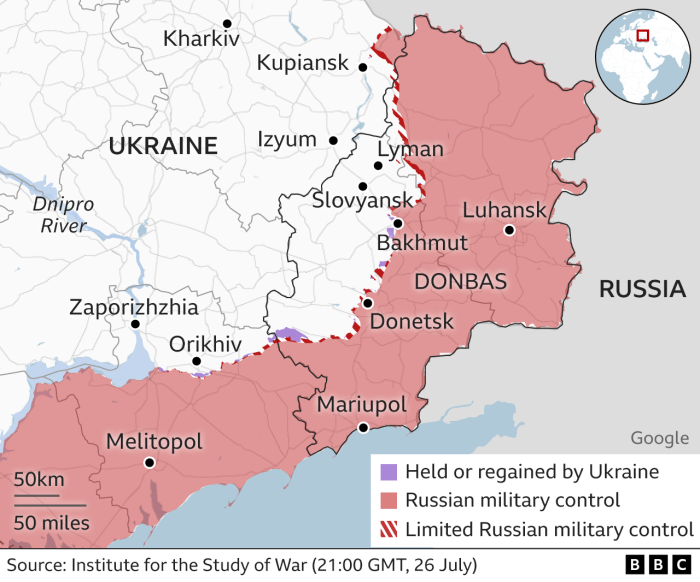
The conflict in Ukraine continues to evolve rapidly, with significant shifts in the military landscape occurring almost daily. Analyzing the recent events requires careful consideration of the strategies employed by both sides, the impact of international aid, and the ongoing struggle for territorial control. This section will provide a concise overview of the key developments over the past month, focusing on these crucial aspects.
Significant Military Events (Last Month)
The past month has witnessed intensified fighting in several key areas. Early in the period, there were reports of increased Russian shelling in eastern Ukraine, particularly around Bakhmut, which saw heavy fighting and a reported slow but steady advance by Russian forces. Simultaneously, Ukrainian forces conducted counter-offensive operations in the south, focusing on the Zaporizhzhia region, aiming to disrupt Russian supply lines and potentially recapture occupied territory. Mid-month saw a notable increase in drone attacks targeting both military and civilian infrastructure within Russia, prompting retaliatory strikes from Russia on Ukrainian cities. Towards the end of the month, reports indicated a renewed focus on the eastern front, with both sides engaging in intense artillery duels and small-scale ground offensives. The exact extent of territorial gains or losses during this period remains subject to ongoing verification from independent sources.
Military Strategies: A Comparison
Russia’s military strategy has largely focused on a combination of artillery barrages, combined arms assaults (involving infantry, tanks, and artillery), and the utilization of Wagner Group mercenaries in areas requiring intense close-quarters combat. Their strategy has often involved attempts to encircle and overwhelm Ukrainian forces through sheer firepower and attrition. In contrast, Ukraine has employed a more agile and adaptable strategy, focusing on utilizing Western-supplied precision weaponry to target Russian command and control centers, logistics hubs, and ammunition depots. They have also effectively integrated drones and other unmanned systems into their operations, disrupting Russian advances and gathering intelligence. Ukrainian counter-offensives have prioritized achieving localized breakthroughs rather than large-scale advances, aiming to deplete Russian resources and manpower.
Impact of International Military Aid
The influx of international military aid has been a crucial factor shaping the conflict. The provision of advanced weaponry, including long-range artillery systems, air defense systems, and armored vehicles, has significantly enhanced Ukraine’s ability to defend against Russian aggression and conduct effective counter-offensives. This aid has not only improved Ukraine’s defensive capabilities but has also allowed them to target Russian forces and infrastructure with greater precision and effectiveness, potentially altering the balance of power on the battlefield. However, the continued need for substantial military aid highlights the ongoing challenges and the protracted nature of the conflict.
Territorial Control
The following table provides a simplified overview of territorial control. It is important to note that the situation is fluid and subject to change. Verification of claims from both sides remains a challenge for independent observers.
| Region | Ukrainian Control | Russian Control | Disputed/Contested |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Ukraine (Donbas) | Parts of Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts | Significant portions of Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts | Ongoing intense fighting in several areas. |
| Southern Ukraine | Significant portions of Kherson and Zaporizhzhia oblasts | Significant portions of Kherson and Zaporizhzhia oblasts, including Crimea | Active fighting and counter-offensive operations. |
| Northern Ukraine | Majority of territory | Minimal | Relatively stable, with localized incidents. |
| Central Ukraine | Majority of territory | Minimal | Relatively stable. |
Humanitarian Crisis
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has triggered a profound humanitarian crisis, impacting millions of civilians. The scale of suffering is immense, demanding an urgent and sustained international response. The destruction of infrastructure, displacement of populations, and ongoing violence have created widespread hardship and suffering.
The challenges facing humanitarian organizations are substantial and multifaceted, hindering effective aid delivery and exacerbating the crisis.
Civilian Casualties and Displacement, Ukraine news
The war has resulted in a tragic loss of civilian life and widespread displacement. While precise figures are difficult to obtain due to the ongoing conflict and challenges in data collection, the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) has documented thousands of civilian casualties, including many children. Millions have been forced to flee their homes, seeking refuge within Ukraine or in neighboring countries. The true numbers are likely significantly higher, as many incidents remain unreported or undocumented due to the intensity of fighting and limited access to affected areas. This massive displacement has placed immense strain on resources in host communities and created a complex web of humanitarian needs.
Challenges Faced by Humanitarian Organizations
Humanitarian organizations face numerous obstacles in their efforts to deliver aid effectively. These include active conflict zones restricting access to vulnerable populations, damaged infrastructure hampering logistics, and security concerns for aid workers. Funding shortages are also a major constraint, limiting the scale and scope of humanitarian operations. Bureaucratic hurdles and navigating complex political landscapes further complicate the process of delivering essential aid to those in need. The destruction of vital infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and communication networks, severely impacts the ability to reach affected communities. Moreover, the constant threat of shelling and violence creates significant safety risks for humanitarian workers.
Long-Term Effects on Ukrainian Well-being
The long-term consequences of the war on the Ukrainian population’s well-being are likely to be severe and far-reaching. The trauma of war, including witnessing violence, displacement, and loss of loved ones, will have profound psychological and emotional impacts on individuals and communities for years to come. The destruction of homes, businesses, and infrastructure will have devastating economic consequences, leading to widespread poverty and unemployment. Access to essential services such as healthcare and education has been severely disrupted, further compounding the long-term challenges. The mental health needs of the population, especially children and families who have experienced violence or loss, will require sustained and extensive support for decades to come. Rebuilding the nation’s infrastructure and economy will be a monumental task requiring significant international investment and collaboration.
Most Pressing Humanitarian Needs in Ukraine
The following points highlight the most urgent humanitarian needs in Ukraine:
- Food and clean water: Millions are facing food insecurity and lack access to safe drinking water.
- Shelter and housing: Homes have been destroyed, leaving many without adequate shelter.
- Medical care and essential medicines: Access to healthcare is limited, and essential medicines are in short supply.
- Protection for vulnerable groups: Women, children, and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to exploitation and violence.
- Mental health support: The psychological impact of war requires significant mental health services.
- Cash assistance: Providing financial support allows individuals to meet their basic needs.
- Reconstruction and recovery: The long-term rebuilding of infrastructure and communities is critical.
International Response
The international community’s response to the conflict in Ukraine has been multifaceted and significant, encompassing military aid, economic sanctions, humanitarian assistance, and diplomatic initiatives. The scale and nature of these responses reflect the global condemnation of Russia’s actions and the international commitment to supporting Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. However, the effectiveness of these responses remains a subject of ongoing debate and analysis.
Key International Actors and Their Roles
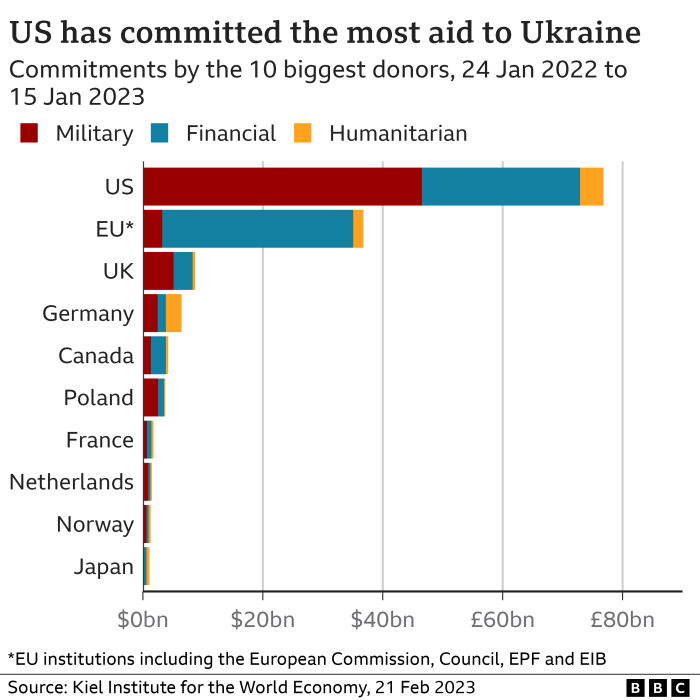
The conflict has involved a wide array of international actors, each playing a distinct role. The United States, for example, has provided substantial military and financial aid to Ukraine, becoming a key player in supporting its defense efforts. The European Union has implemented extensive sanctions against Russia and provided significant humanitarian and financial assistance to Ukraine. NATO, while not directly involved militarily, has provided crucial intelligence support and strengthened its eastern flank’s defenses. Individual nations such as the United Kingdom, Canada, and Poland have also provided significant military, financial, and humanitarian aid. The United Nations, meanwhile, has focused on humanitarian relief and diplomatic efforts to de-escalate the conflict, though its effectiveness has been limited by Russia’s veto power in the Security Council. China’s role is complex, maintaining a neutral stance while increasing economic ties with Russia.
Comparison of Sanctions Imposed on Russia
The sanctions imposed on Russia by various countries and international organizations have varied in scope and severity. The EU, US, UK, and Canada have implemented comprehensive sanctions targeting key sectors of the Russian economy, including finance, energy, and technology. These sanctions include asset freezes, travel bans, and restrictions on trade. The EU’s sanctions, for instance, have focused on limiting access to the SWIFT international payment system and targeting specific individuals and entities linked to the Russian government and military. The US sanctions have focused on targeting specific oligarchs and financial institutions, aiming to disrupt Russia’s access to global financial markets. While some countries have implemented more targeted sanctions, the overall aim is to cripple Russia’s economy and exert pressure on the Kremlin to cease hostilities. The effectiveness of these sanctions is a subject of ongoing debate, with some arguing that they have had a significant impact on the Russian economy, while others point to Russia’s ability to mitigate some of the effects.
Effectiveness of Diplomatic Efforts
Diplomatic efforts to resolve the conflict have so far yielded limited success. The UN and other international organizations have facilitated various rounds of talks between Russia and Ukraine, but these have largely failed to produce a lasting ceasefire or a comprehensive peace agreement. Russia’s demands and actions have consistently undermined these efforts, highlighting the challenges of achieving a diplomatic solution in the face of a belligerent actor. While some channels of communication remain open, the prospects for a swift diplomatic resolution remain uncertain. The ongoing conflict underscores the limitations of diplomacy when one party is unwilling to negotiate in good faith.
International Responses Categorized
| Military Response | Economic Response | Humanitarian Response | Diplomatic Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Military aid (weapons, training) provided by the US, UK, EU members, and others. Intelligence sharing and logistical support. | Sanctions targeting Russian banks, energy sector, individuals, and specific industries. Trade restrictions and asset freezes. | Provision of food, medical supplies, shelter, and financial aid to Ukrainian refugees and internally displaced persons by numerous countries and international organizations like the UN and Red Cross. | Negotiations facilitated by the UN, OSCE, and individual countries. Attempts at mediation and dialogue to achieve a ceasefire and peaceful resolution. |
Economic Impact: Ukraine News
The war in Ukraine has had a devastating impact on the country’s economy, rippling outwards to significantly affect global energy markets and food security. The scale of destruction to infrastructure, the displacement of millions, and the disruption of agricultural production and industrial activity have created a profound economic crisis. Understanding these consequences is crucial for assessing the long-term ramifications of the conflict.
Ukraine’s Economic Consequences
The immediate impact on Ukraine’s economy has been catastrophic. The World Bank estimates a contraction of over 45% in GDP in 2022. This is a result of widespread damage to infrastructure, including critical energy, transportation, and agricultural facilities. Businesses have been forced to close, and investment has plummeted. The ongoing conflict continues to hinder economic activity, with ongoing disruptions to supply chains and labor shortages further exacerbating the situation. The destruction of agricultural lands and the inability to plant and harvest crops have led to significant losses in agricultural output, a crucial sector of Ukraine’s economy. The long-term recovery will require substantial investment in rebuilding infrastructure and restoring economic activity. The scale of this undertaking is monumental, and the timeline for recovery remains uncertain, heavily dependent on the cessation of hostilities and the availability of sustained international support.
Impact on Global Energy Markets and Food Security
Ukraine and Russia are major exporters of wheat, corn, sunflower oil, and other agricultural commodities. The war has disrupted these supply chains, leading to significant price increases and shortages globally. This has disproportionately impacted vulnerable populations in developing countries reliant on these exports. The conflict has also exacerbated existing energy price pressures, particularly for natural gas, as Russia is a major global supplier. Sanctions imposed on Russia have further disrupted energy markets, leading to increased energy prices and impacting inflation worldwide. The interconnectedness of global supply chains means that the consequences of the war in Ukraine extend far beyond its borders, impacting the availability and affordability of essential goods for millions worldwide. For example, the price spikes in wheat have led to food insecurity in several North African and Middle Eastern countries.
International Financial Assistance to Ukraine
The international community has responded with significant financial assistance to Ukraine. The European Union, the United States, and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) have provided billions of dollars in loans, grants, and other forms of financial aid. This assistance is crucial for supporting Ukraine’s government and its people during the conflict and for financing the reconstruction efforts once the war ends. However, the scale of the economic devastation necessitates continued and potentially increased international support to ensure Ukraine’s economic recovery and stability. This aid is not only vital for Ukraine’s immediate needs but also plays a role in preventing further regional instability. The ongoing provision of financial support helps to maintain essential public services, prevent further economic collapse, and foster hope for a future recovery.
Key Economic Indicators: Before and During the Conflict
| Indicator | Pre-War (2021 Estimate) | 2022 Estimate | 2023 Projection (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (%) | 3.4% | -45% (World Bank Estimate) | Variable, dependent on conflict resolution and international aid |
| Inflation (%) | 10% | >20% (Estimate) | High, but potentially declining with aid and stabilization |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 9% | Significantly Increased (uncertain due to displacement and business closures) | High, but likely to vary regionally |
| Exchange Rate (UAH/USD) | ~28 | Fluctuating, significantly devalued | Uncertain, dependent on international reserves and market conditions |
Information Warfare and Propaganda
The conflict in Ukraine has been accompanied by a massive and sophisticated information war, with both sides employing various tactics to shape public opinion and influence the narrative of the conflict. This battle for hearts and minds takes place not only on traditional media but also, perhaps more significantly, on social media platforms, where misinformation can spread rapidly and widely. Understanding the strategies and challenges involved is crucial to navigating the complex information landscape surrounding the war.
Examples of Disinformation and Propaganda
Both Russia and Ukraine have engaged in the dissemination of disinformation and propaganda. Russian state media, for instance, has consistently portrayed the conflict as a necessary “special military operation” to “denazify” Ukraine, downplaying civilian casualties and presenting a distorted view of Ukrainian intentions. Conversely, Ukrainian sources have emphasized Russian atrocities and presented a narrative of heroic resistance against an unprovoked aggressor, sometimes employing emotionally charged imagery and appeals to national identity. Examples of disinformation include fabricated accounts of atrocities, manipulated images and videos, and the spread of conspiracy theories aimed at discrediting the opposing side. The use of bots and troll farms to amplify certain narratives and suppress others is also a significant element of this information war.
The Role of Social Media in Shaping Public Opinion
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Telegram have become crucial battlegrounds in the information war. Their speed and reach allow disinformation to spread rapidly, bypassing traditional fact-checking mechanisms. Algorithms that prioritize engagement can inadvertently amplify misleading or false narratives, further contributing to the spread of misinformation. The ease with which manipulated media can be created and shared, coupled with the challenges of verifying information in real-time, makes social media a particularly fertile ground for propaganda. Consequently, public perception of the conflict is heavily influenced by the information—and misinformation—circulating on these platforms. The emotional nature of the conflict further complicates the issue, as users are more likely to share information that confirms their pre-existing beliefs, regardless of its veracity.
Challenges of Verifying Information and Combating Misinformation
Verifying information amidst the deluge of competing narratives presents significant challenges. The rapid pace of events, coupled with the deliberate obfuscation of information by both sides, makes it difficult for fact-checkers and journalists to keep up. The sophisticated techniques used to create and disseminate disinformation, such as deepfakes and manipulated videos, further complicate the process. Moreover, the sheer volume of information circulating online makes it difficult to identify and address every instance of misinformation. Combating misinformation requires a multi-faceted approach, including improved media literacy education, greater transparency from social media companies, and stronger efforts from fact-checking organizations. International cooperation is also essential to coordinate efforts to counter disinformation campaigns.
Different Narratives Presented by Various Media Outlets
Different media outlets present significantly different narratives of the conflict, reflecting their geographical location, political leanings, and access to information. State-controlled media in Russia often presents a pro-Kremlin perspective, while Western media outlets tend to offer a more critical view of Russia’s actions. Independent media outlets strive for objectivity but often face challenges in accessing information and verifying sources in a war zone. These differing narratives contribute to a fragmented information landscape, making it difficult for individuals to form a comprehensive and unbiased understanding of the conflict. The contrast in reporting styles, emphasis on specific events, and selection of sources highlights the complexities of interpreting information related to the war.
Refugee Crisis

The war in Ukraine has triggered one of the fastest-growing refugee crises in recent history, forcing millions to flee their homes in search of safety and security. The scale and speed of displacement have placed immense strain on neighboring countries and international organizations alike, highlighting the complex challenges involved in providing humanitarian assistance and managing large-scale population movements. Understanding the scope of this crisis, the challenges it presents, and its long-term implications is crucial for effective response and planning.
Scale and Destinations of Ukrainian Refugees
As of late 2023, the UNHCR estimates that over 8 million Ukrainian refugees have fled the country since the start of the full-scale invasion. The majority have sought refuge in neighboring countries, particularly Poland, which has received the largest influx. Significant numbers have also relocated to Romania, Moldova, Hungary, and Germany, among others. The exact numbers fluctuate daily, reflecting the ongoing conflict and the dynamic nature of displacement. Many refugees have also moved internally within Ukraine to safer regions. The initial wave of refugees was largely composed of women and children, as men of fighting age were often unable or unwilling to leave.
Challenges Faced by Host Countries
Hosting millions of refugees presents significant challenges for recipient nations. These include the strain on public services such as housing, healthcare, and education; increased pressure on the labor market; potential social tensions; and the logistical complexities of providing basic necessities like food, water, and shelter. Many host countries have shown remarkable generosity and resilience in their response, but the sheer scale of the crisis continues to test their capacities. For example, Poland’s infrastructure and social services experienced considerable strain in the initial months following the invasion. The long-term economic and social integration of refugees also poses a significant challenge.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of this refugee crisis are multifaceted and far-reaching. For refugees, the trauma of displacement, separation from loved ones, and the uncertainty of their future can have profound psychological and social consequences. Access to education, employment, and healthcare in host countries will be crucial for their successful integration and long-term well-being. For host countries, the integration of large numbers of refugees can create both opportunities and challenges, impacting demographics, labor markets, and social cohesion. Sustained international support and coordinated efforts will be essential to mitigate potential negative impacts and foster successful integration. Successful integration of refugees could enrich the cultural landscape and contribute to the economy of host countries, but it requires careful planning and substantial investment.
Refugee Distribution and Challenges
| Country | Approximate Number of Refugees (as of late 2023 – estimates vary) | Major Challenges | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poland | Over 1.5 million | Strain on housing, healthcare, education; integration challenges; potential for social tensions. | Poland has demonstrated significant resilience and generosity in its response. |
| Germany | Over 1 million | Strain on housing, integration of refugees into the labor market; language barriers. | Germany has a history of accepting refugees, but the sheer scale presents a new challenge. |
| Romania | Over 500,000 | Strain on public services, particularly in border regions; managing the influx of refugees. | Romania has shown strong solidarity with Ukraine and its people. |
| Moldova | Over 100,000 | Disproportionately high number of refugees relative to its population; economic strain; limited resources. | Moldova, despite its own economic challenges, has offered significant support to Ukrainian refugees. |
Political Implications
The war in Ukraine has profoundly reshaped the country’s political landscape and introduced significant instability into the broader regional context. The conflict has intensified existing political fault lines, spurred a dramatic shift in power dynamics, and created a complex web of international political maneuvering.
The impact on Ukraine’s political system is multifaceted. The initial shock of the invasion led to a rapid consolidation of power around President Zelenskyy, who has garnered significant international support. However, this unity is not without its challenges. The ongoing war necessitates difficult decisions, including wartime governance, potentially leading to increased executive power and a diminished role for traditional political opposition. The war has also highlighted the limitations of pre-war political structures and practices, necessitating reforms to address weaknesses exposed by the conflict.
Impact on Ukraine’s Political System
The war has significantly altered Ukraine’s political system. The state of martial law has temporarily suspended certain civil liberties, and the focus has shifted decisively towards national defense and security. The pre-war political divisions, while still present, are largely overshadowed by the urgent need for national unity against a common enemy. The effectiveness of post-war political reconstruction will heavily depend on the successful integration of displaced populations and the establishment of credible mechanisms for accountability and reconciliation. The experience of wartime governance could lead to lasting changes in the balance of power between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, potentially resulting in a more centralized system.
Potential for Regional Political Instability
The war in Ukraine has dramatically increased the potential for regional political instability. Neighboring countries are grappling with the influx of refugees, economic disruptions, and security concerns. The conflict’s spillover effects could destabilize fragile governments and exacerbate existing tensions. The potential for further escalation, including the involvement of other actors, adds to the uncertainty and poses a serious threat to regional peace and security. This instability is not limited to immediate neighbors; the global implications of the war, including disruptions to energy markets and increased international tensions, contribute to a broader sense of insecurity. The war’s long-term effects on regional political dynamics are difficult to predict but will undoubtedly be profound.
Key Political Actors and Their Agendas
The key political actors involved in the conflict are numerous and their agendas complex. President Volodymyr Zelenskyy leads Ukraine, striving to defend his country’s sovereignty and territorial integrity while securing international support. Vladimir Putin, President of Russia, seeks to achieve his geopolitical objectives, which include undermining Ukraine’s sovereignty and expanding Russian influence in the region. NATO and the European Union are crucial actors providing military and humanitarian assistance to Ukraine and imposing sanctions on Russia. Other actors, such as the United States and China, play significant roles through their diplomatic efforts and economic leverage. The agendas of these actors are multifaceted and often intertwined, leading to a highly dynamic and unpredictable political landscape.
Timeline of Significant Political Events
The following timeline highlights key political developments related to the conflict:
- February 2014: Annexation of Crimea by Russia following the Ukrainian Revolution.
- April 2014: Start of the War in Donbas.
- February 2022: Full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine.
- March 2022: International sanctions imposed on Russia.
- September 2022: Referendums held in occupied Ukrainian territories.
- October 2022: Escalation of fighting and missile strikes on Ukrainian infrastructure.
- Ongoing: International efforts to negotiate a ceasefire and resolve the conflict.
This timeline represents a selection of pivotal events; numerous other significant political developments have occurred throughout the conflict. The evolving situation continues to generate new political challenges and necessitates constant reassessment of the actors and their shifting agendas.
Reconstruction and Recovery
The scale of destruction in Ukraine necessitates a massive and multifaceted reconstruction effort, one that will require significant international cooperation and sustained commitment over many years. Rebuilding Ukraine will not simply be about restoring physical infrastructure; it will also involve revitalizing the economy, addressing social trauma, and fostering a sense of national unity and hope. The challenges are immense, but the potential for a rebuilt Ukraine, stronger and more resilient than before, is equally significant.
The task of rebuilding Ukraine’s infrastructure presents a monumental challenge. The war has inflicted widespread damage on homes, businesses, schools, hospitals, and critical infrastructure like power grids, transportation networks, and water systems. The sheer geographical extent of the damage, coupled with the ongoing conflict in some areas, makes accurate assessment and prioritization of repair work incredibly difficult. Furthermore, the destruction is not uniform; some regions have experienced near-total devastation, while others have suffered more localized damage. This necessitates a flexible and adaptable reconstruction strategy that can respond to the specific needs of different communities.
International Aid for Reconstruction
International aid will be crucial in financing and implementing Ukraine’s reconstruction. The scale of the required investment dwarfs Ukraine’s own resources. Various international organizations, including the European Union, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund, are already providing financial and technical assistance. However, the level of funding needed to address the complete scope of reconstruction remains significantly underfunded. Successful aid disbursement will require a transparent and accountable system to ensure that funds are used effectively and reach those who need them most. Examples of successful international aid initiatives in post-conflict reconstruction, such as the Marshall Plan following World War II, can offer valuable lessons and frameworks for Ukraine’s recovery. The Marshall Plan, for example, involved not only financial aid but also technical expertise and institutional capacity building, all of which will be vital for Ukraine’s long-term recovery.
Social and Economic Implications of Long-Term Reconstruction
The long-term social and economic implications of reconstruction are profound and far-reaching. Rebuilding physical infrastructure is only one part of the equation. The war has caused widespread displacement, loss of life, and deep psychological trauma, all of which will have long-lasting impacts on society. Addressing these social needs through investment in mental health services, education, and social welfare programs is essential for fostering social cohesion and stability. Economically, reconstruction offers an opportunity to modernize Ukraine’s infrastructure and create new economic opportunities. This includes investment in renewable energy sources, digital technologies, and sustainable agricultural practices. However, this requires careful planning and coordination to avoid exacerbating existing economic inequalities and to ensure that the benefits of reconstruction are shared widely across the population. The successful integration of returning refugees into the workforce and the economy will also be a critical element of long-term economic recovery.
A Plan for Post-Conflict Recovery
A successful post-conflict recovery plan requires a phased approach, prioritizing immediate needs while laying the groundwork for long-term sustainable development. This will require strong leadership, international cooperation, and the active participation of Ukrainian citizens.
The following key steps are crucial:
- Immediate Needs: Addressing immediate humanitarian needs, including providing food, shelter, medical care, and security for displaced persons and those affected by the conflict. This phase will involve the rapid mobilization of international aid and the coordination of relief efforts.
- Stabilization and Security: Ensuring the security and stability of the country, including demilitarization, disarmament, and the establishment of effective governance structures. This will involve cooperation with international partners to ensure a secure and peaceful environment.
- Infrastructure Repair and Reconstruction: Prioritizing the repair and reconstruction of essential infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, water systems, and housing. This will require significant investment and technical expertise, with a focus on sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
- Economic Recovery and Development: Implementing economic reforms to stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and attract foreign investment. This will involve promoting private sector development, improving the business environment, and diversifying the economy.
- Social and Psychological Healing: Providing psychosocial support and mental health services to those affected by the conflict, as well as promoting social cohesion and reconciliation. This will require investment in education, social welfare programs, and community-based initiatives.
- Institutional Reform and Good Governance: Strengthening democratic institutions, promoting good governance, and combating corruption. This will involve reforms to ensure transparency, accountability, and the rule of law.
- International Cooperation and Partnership: Maintaining strong international partnerships to secure continued financial and technical assistance, and to ensure ongoing monitoring and evaluation of reconstruction efforts. This will involve close collaboration with international organizations and donor countries.
Legal and Accountability Aspects
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has raised significant concerns regarding international law and the pursuit of accountability for alleged war crimes and other atrocities. Numerous international legal frameworks are applicable, and various mechanisms are being employed to investigate and potentially prosecute those responsible. However, the complexities of the situation present considerable legal challenges.
Applicable International Legal Frameworks
The conflict in Ukraine falls under the purview of several key international legal instruments. The Geneva Conventions of 1949, along with their Additional Protocols, provide the foundational legal framework for the protection of civilians and combatants during armed conflict. These conventions prohibit acts such as torture, cruel treatment, and the targeting of civilians. The Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC) establishes the jurisdiction of the Court over war crimes, crimes against humanity, genocide, and the crime of aggression. Ukraine has accepted the ICC’s jurisdiction, and the Court has opened an investigation into alleged crimes committed on its territory since November 2013. Furthermore, principles of customary international humanitarian law (IHL), which are binding on all states regardless of ratification of specific treaties, also play a crucial role.
Potential for War Crimes Investigations and Prosecutions
The ICC’s investigation is a primary mechanism for pursuing accountability. Numerous allegations of war crimes have emerged, including the targeting of civilians, indiscriminate attacks, the destruction of civilian infrastructure, and the alleged use of prohibited weapons. National jurisdictions also have a role to play. Ukraine itself is conducting its own investigations, and several other countries have initiated investigations into alleged crimes committed by their own nationals or related to their citizens. International cooperation is vital for the success of these investigations, including the sharing of evidence and witness testimony. The sheer volume of alleged atrocities, the scale of destruction, and the challenges of collecting and preserving evidence present significant logistical and procedural hurdles.
Mechanisms for Ensuring Accountability for Atrocities
Beyond the ICC and national courts, various other mechanisms are being utilized to document and address atrocities. The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) is actively monitoring the human rights situation and documenting alleged violations. Independent investigative bodies and international organizations, such as Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International, are also collecting evidence and reporting on alleged war crimes. These organizations play a crucial role in informing the international community and building pressure for accountability. The establishment of international hybrid tribunals or commissions of inquiry could be considered in the future to address specific aspects of the conflict and supplement the work of the ICC and national courts.
Legal Challenges in Prosecuting War Crimes
Prosecuting war crimes in the context of the Ukraine conflict presents numerous legal challenges. Gathering sufficient evidence to meet the high burden of proof required in international criminal proceedings is a major hurdle. Witness protection and security concerns are paramount, given the ongoing conflict and potential reprisals against those who cooperate with investigations. Determining the chain of command and establishing individual criminal responsibility can be extremely complex, particularly in cases involving large-scale atrocities or decentralized command structures. Jurisdictional issues can also arise, particularly when determining which court or tribunal has the authority to prosecute specific individuals or cases. Furthermore, the political context of the conflict can significantly influence the pace and outcome of investigations and prosecutions, creating pressure and challenges for judicial independence.
Last Recap
The conflict in Ukraine continues to unfold, demanding sustained attention and concerted international action. The humanitarian crisis remains dire, requiring ongoing aid and support for those affected. The long-term implications, from economic recovery to ensuring accountability for war crimes, will necessitate sustained commitment from the international community. While the path to resolution remains uncertain, a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted dimensions of this conflict is essential for informed engagement and effective responses.






